.png&w=3840&q=75)
Summarize this post with AI
What if your business could predict customer churn before it happens, detect fraud in milliseconds, or reduce equipment downtime by 30%? This is exactly what Data Science AI makes possible, and it's no longer reserved for tech giants. In 2026, Data Science AI (DS AI) sits at the center of every major business transformation. According to McKinsey, organizations that adopt data-driven strategies are 23x more likely to acquire customers and 19x more likely to achieve profitability.In this comprehensive guide, you'll learn exactly what Data Science AI is, how the DS AI process works step by step, which tools dominate the field, and how companies across every industry are generating measurable ROI. Whether you're a business decision-maker, a student entering the field, or a professional looking to upskill this guide is your starting point.
Pro Tip
Bookmark this page! We'll cover everything from the basics of DS AI to advanced implementation strategies, real-world case studies, and salary expectations for 2026.
What is Data Science AI?
Data Science AI is the integration of artificial intelligence techniques such as machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing with the core practices of data science, including data collection, cleaning, statistical modeling, and visualization, to extract actionable insights and automate intelligent decision-making at scale.
How DS AI Differs from Traditional Data Science
Dimension | Traditional Data Science | Data Science AI |
Decision Making | Human-driven insights | Automated AI recommendations |
Scale | Handles thousands of records | Processes billions of data points |
Speed | Reports in hours/days | Real-time predictions in milliseconds |
Adaptability | Static models | Self-learning, continuously improving |
Output | Dashboards & reports | Autonomous actions + explanations |
Why Businesses Need DS AI Now
The data explosion is real. By 2026, the world generates over 120 zettabytes of data per year. Without AI, businesses simply cannot process, analyze, or act on this volume fast enough to stay competitive.
Cost reduction: AI-driven automation cuts operational costs by up to 40% in manufacturing. [INSERT SOURCE: Deloitte AI Survey]
Revenue growth: Personalization powered by DS AI increases e-commerce revenue by 10–30%. [INSERT SOURCE: Forrester Research]
Risk mitigation: Fraud detection models reduce financial losses by 50–70% for banking institutions.
Competitive advantage: Companies using DS AI outperform peers by 5–8% in productivity.
Learn how Samta.ai's AI & Data Science Services help businesses unlock the full potential of DS AI.
The Evolution of Data Science AI
To understand where DS AI is today, we need to trace its rapid evolution over the past decade.
Period | Key Development |
Pre-2015 | Traditional statistical modeling; Hadoop/MapReduce for big data analytics; R and SAS dominate. |
2015–2018 | Rise of Python and TensorFlow; deep learning breakthroughs in image recognition. Cloud Platforms democratize ML. |
2019–2021 | GPT models transform NLP; AutoML tools emerge; MLOps becomes a discipline; COVID-19 accelerates AI adoption. |
2022–2024 | Generative AI explosion (ChatGPT, Gemini); multimodal models; AI regulation begins in EU and US. |
2025–2026 | Agentic AI systems; real-time edge AI; AI-powered data engineering; explainable AI (XAI) mandates in regulated industries. |
The most significant shift? DS AI is no longer a back-office function it's a core business strategy. According to Gartner, 87% of data science projects never made it to production pre-2020. Today, with MLOps and cloud infrastructure, that number has dropped dramatically.
Core Components of DS AI
DS AI is not a single technology it's an ecosystem of interconnected disciplines working together. Here are the four foundational pillars:
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning (ML) is the engine of DS AI. ML algorithms learn patterns from historical data and use those patterns to make predictions or decisions on new data without being explicitly programmed for each scenario.
Supervised Learning: Trains on labeled data (e.g., spam detection, credit scoring). Algorithms: Linear Regression, Random Forest, XGBoost.
Unsupervised Learning: Finds hidden patterns in unlabeled data (e.g., customer segmentation). Algorithms: K-Means, DBSCAN, PCA.
Reinforcement Learning: Learns through trial and reward (e.g., autonomous driving, game AI). Algorithms: Q-Learning, PPO.
Deep Learning: Multi-layered neural networks for complex tasks (e.g., image recognition, NLP). Frameworks: TensorFlow, PyTorch.
Artificial Intelligence Technologies
AI technologies extend ML capabilities into human-like reasoning and language understanding:
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Powers chatbots, sentiment analysis, and document extraction. Examples: BERT, GPT-4, LLaMA.
Computer Vision: Enables machines to interpret images and video. Used in quality control, medical imaging, security.
Generative AI: Creates new content (text, images, code). Transforming marketing, product design, and software development.
Statistical Analysis & Modeling
Before any ML model runs, solid statistical modeling and exploratory data analysis (EDA) ensure your data is understood and your models are valid. This includes hypothesis testing, A/B testing, regression analysis, and time series forecasting.
Data Engineering Infrastructure
Even the best AI models fail without clean, accessible data. Data engineering for the pipelines, warehouses, and orchestration layers is the backbone of every successful DS AI initiative. Tools include Apache Spark, dbt, Airflow, Snowflake, and Databricks.
Key Takeaway
DS AI combines machine learning, AI technologies, statistical rigor, and engineering infrastructure. Weakness in any one area limits the entire system. Invest in all four pillars for sustainable success.
The Complete 7-Step DS AI Process
Successful DS AI projects follow a structured workflow. Each step builds on the last skipping steps is the reason AI projects fail. Here is the complete DS AI process used by leading organizations:
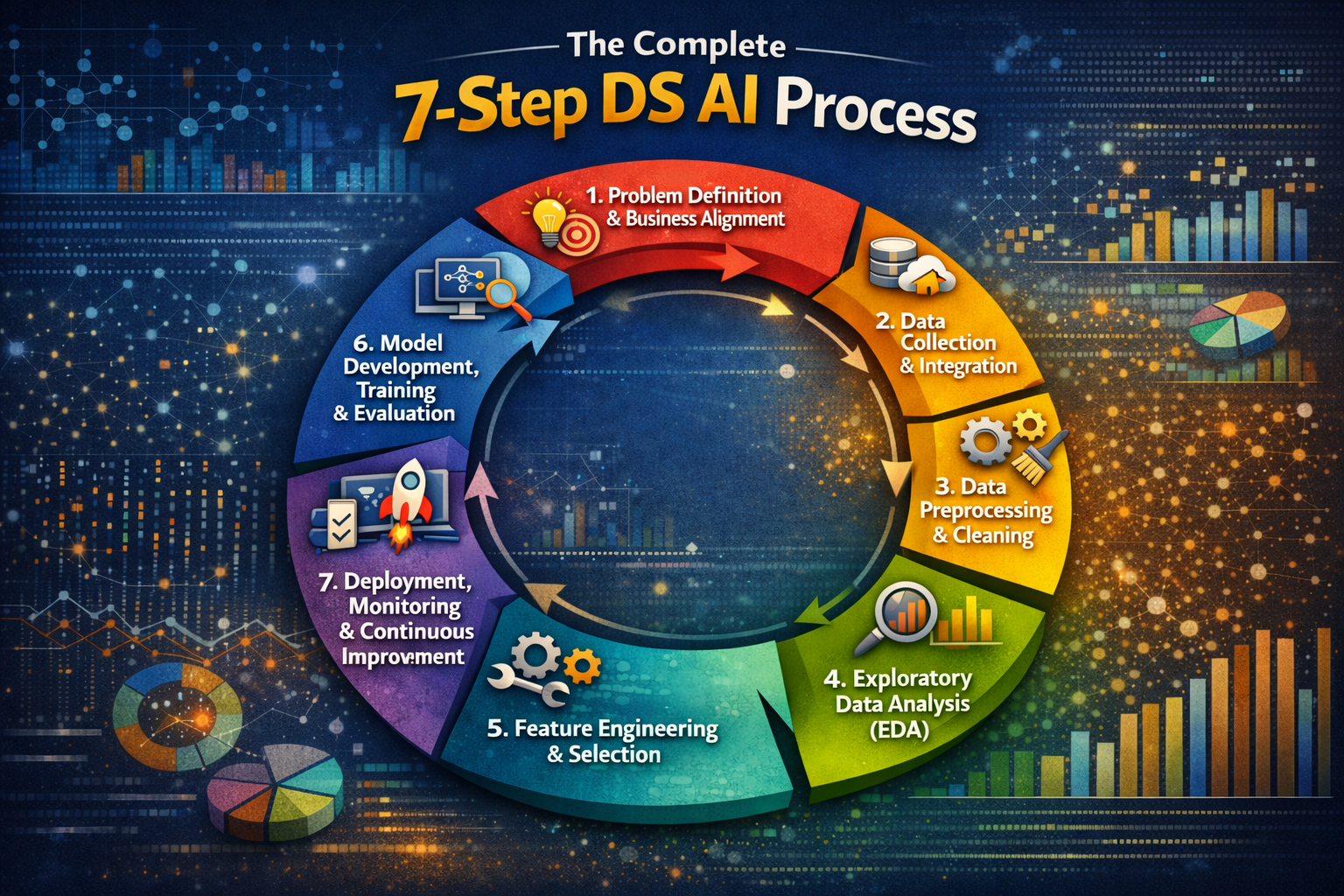
Step 1: Problem Definition & Business Alignment
What it is: Translating a business challenge into a precise, measurable data science problem statement. This step defines success criteria, stakeholders, timeline, and budget.
Why it matters: According to Towards Data Science, 85% of AI failures stem from poorly defined problems. Without clarity here, the entire project drifts.
Tools: Business Model Canvas, SMART Goals framework, stakeholder interview templates.
Common challenge: Stakeholders often describe symptoms ('sales are dropping') rather than root causes. Push for specific, quantifiable objectives.
Best practice: Define success before you start. Example: Reduce customer churn by 15% within 6 months using a predictive model with ≥80% accuracy.
Real-world example: A retail chain defined the problem as 'predict which customers will cancel their subscription in the next 30 days' not just 'reduce churn.' This specificity led to a 22% churn reduction in 4 months.
Step 2: Data Collection & Integration
What it is: Gathering data from all relevant internal and external sources databases, APIs, IoT sensors, web scraping, CRM systems, social media, and third-party data providers.
Why it matters: Your model can only be as good as your data. Incomplete or biased data leads to inaccurate, unreliable predictions.
Tools: Apache Kafka (real-time streaming), AWS Glue (ETL), REST APIs, Scrapy (web data), Fivetran (data integration).
Common challenge: Data silos across departments. Marketing has CRM data; operations has ERP data; finance has billing data and none of it talks to each other.
Best practice: Build a unified data lake or lakehouse architecture on AWS S3, Azure Data Lake, or Google Cloud Storage to centralize all data sources.
Real-world example: A healthcare provider integrated EHR data, lab results, wearable device data, and pharmacy records into a single pipeline enabling 30% faster patient risk stratification.
Step 3: Data Preprocessing & Cleaning
What it is: Transforming raw, messy data into a clean, consistent, analysis-ready format. This includes handling missing values, removing duplicates, encoding categorical variables, and normalizing numerical features.
Why it matters: Data scientists spend 60–80% of their time on this step.Garbage in = garbage out.
Tools: Pandas, NumPy (Python), dbt (SQL-based transformation), Great Expectations (data validation), OpenRefine.
Common challenge: Missing data handling. Options include imputation (mean, median, KNN), forward-fill for time series, or dropping rows each with trade-offs.
Best practice: Document every transformation in a data lineage tool. Future team members (and auditors) need to trace exactly what was changed and why.
Step 4: Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
What it is: Visually and statistically exploring your dataset to understand distributions, correlations, outliers, and relationships between variables before modeling.
Why it matters: EDA often reveals insights that change the entire modeling approach. You may discover that the 'key' variable you planned to use has 40% missing data or that two variables are so correlated they'll cause multicollinearity.
Tools: Seaborn, Matplotlib, Plotly (Python), Tableau, Power BI, data-profiling (automated EDA).
Best practice: Always check class imbalance in classification problems. If 98% of fraud cases are 'not fraud,' a naive model that always says 'not fraud' achieves 98% accuracy but zero utility.
Step 5: Feature Engineering & Selection
What it is: Creating new variables (features) from raw data and selecting the most predictive ones to feed into the model. This is where domain expertise meets data science.
Why it matters: Feature engineering is often the single biggest driver of model performance more impactful than the choice of algorithm.
Tools: Scikit-learn (Python), FeatureTools (automated feature engineering), SHAP (feature importance), Boruta.
Real-world example: An insurance company added a feature called 'time since last claim' seemingly obvious, but previously unused. This single feature improved their fraud detection F1-score by 18%.
Step 6: Model Development, Training & Evaluation
What it is: Selecting appropriate algorithms, training models on historical data, tuning hyperparameters, and rigorously evaluating performance on held-out test data.
Why it matters: Choosing the wrong evaluation metric is catastrophic. Accuracy is misleading for imbalanced datasets. F1-Score, AUC-ROC, or Precision-Recall curves are often more meaningful.
Tools: Scikit-learn, XGBoost, LightGBM, TensorFlow, PyTorch, Optuna (hyperparameter tuning), MLflow (experiment tracking).
Best practice: Always use cross-validation (k-fold) to assess generalization. A model that achieves 99% on training data but 65% on test data is overfitting and worthless in production.
Step 7: Deployment, Monitoring & Continuous Improvement
What it is: Packaging trained models into production APIs, integrating them with business systems, and monitoring for performance degradation over time.
Why it matters: A model that performed perfectly in 2024 may degrade by 2026 due to 'model drift' when real-world data patterns shift away from training data.
Tools: Docker, Kubernetes (containerization), FastAPI (model serving), AWS SageMaker, Azure ML, Grafana + Prometheus (monitoring), Evidently AI (drift detection).
Best practice: Set automated retraining triggers. When model accuracy drops below a predefined threshold, automatically retrain on fresh data and deploy the updated version.
Pro Tip from Our Work with 50+ Clients
The biggest DS AI mistake we see? Teams skip Step 1 (problem definition) and jump straight to Step 6 (modeling). Always spend at least 20% of project time on problem scoping. It saves 80% of the headaches downstream.
Explore Samta.ai's Product Engineering Services to build scalable DS AI solutions on the cloud platform that's right for your organization.
Real-World DS AI Applications by Industry
DS AI is transforming every industry. Here are five detailed case studies showing the problem, solution, implementation, and results:
Retail & E-Commerce: Cart Abandonment Recovery
Problem: An online fashion retailer was experiencing significant revenue loss due to cart abandonment, with an abandonment rate of 73% each year.
DS AI Solution: A real-time predictive model that identifies which users are about to abandon their cart and triggers personalized intervention.
Data collected: Browse history, cart value, time on page, device type, previous purchase history, session behavior.
Model built: XGBoost classifier trained on 18 months of historical session data.
Deployment: Real-time scoring via FastAPI; triggers personalized email/push notification within 8 minutes of abandonment.
Results: Cart recovery rate improved from 5% to 18%. ROI: 790% in year one.
Healthcare: Readmission Prediction
Problem: Hospital readmissions within 30 days cost the US healthcare system. A regional hospital system needed to identify high-risk patients before discharge.
DS AI Solution: An ensemble model combining logistic regression, random forest, and XGBoost, trained on EHR data, lab values, medication history, and social determinants of health (SDOH).
Results: 30-day readmission rate reduced by 23%. Prevented an estimated 1,200 readmissions per year.
Finance: Real-Time Fraud Detection
Problem: A mid-size bank was losing to credit card fraud, with legacy rule-based systems generating 60% false positives frustrating legitimate customers.
DS AI Solution: A deep learning autoencoder trained on normal transaction patterns, combined with a gradient boosting classifier for anomaly detection. Real-time scoring in under 50ms per transaction.
Results: Fraud losses reduced by 67%. False positive rate dropped from 60% to 8%. Customer satisfaction scores improved 22 points on NPS.
Manufacturing: Predictive Maintenance
Problem: Unplanned equipment downtime was costing a heavy equipment manufacturer $180K per hour. Scheduled preventive maintenance was replacing components that still had 40% useful life remaining.
DS AI Solution: IoT sensors on 200+ machines feed vibration, temperature, pressure, and RPM data into a time series forecasting model (LSTM neural network) that predicts failure probability 72 hours in advance.
Results: Unplanned downtime reduced by 37%. Maintenance costs cut 28%. Component waste reduced 41% by only replacing parts near end-of-life.
Marketing: Customer Lifetime Value Prediction
Problem: A SaaS company was spending marketing budget equally across all customers not knowing which ones would become high-value accounts.
DS AI Solution: A Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) prediction model using survival analysis and regression, trained on usage patterns, feature adoption, support tickets, and billing history.
Results: Marketing spend reallocated to top 20% predicted high-CLV prospects. Revenue per marketing dollar increased 3.4x. Customer acquisition cost reduced 45%.
Ready to implement DS AI in your industry? Schedule a free consultation with our team at Samta.ai.
Challenges in Implementing DS AI
In our work with organizations across industries, we encounter the same implementation barriers repeatedly. Understanding these upfront helps you plan more effectively:
Data Quality & Availability
Approximately 80% of the DS AI work is data wrangling not modeling. Incomplete records, inconsistent formats, outdated databases, and siloed systems are universal challenges. Without addressing data quality, even the most sophisticated AI models produce unreliable results.
Talent Shortage & Skill Gaps
The global shortage of data scientists is estimated at 250,000+ professionals in the US alone. Companies struggle not just to hire, but to retain talent as competition from tech giants intensifies.
Samta.ai's Tech Staffing & Augmentation Services help you scale your DS AI team rapidly with pre-vetted experts.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Most established enterprises run DS AI alongside decade-old ERP, CRM, and database infrastructure. Connecting modern AI pipelines to legacy systems requires significant middleware, data transformation, and custom API development.
Cost & ROI Justification
DS AI projects can require significant upfront investment infrastructure, talent, data collection, model development. Business cases must demonstrate clear ROI pathways, which is challenging when benefits are probabilistic ('we predict this will save $X').
Ethical Considerations & Algorithmic Bias
AI models trained on biased historical data can perpetuate or amplify discrimination. A hiring algorithm trained on historical data may de-prioritize women. A lending model may inadvertently redline minority neighborhoods. Proactive bias auditing, fairness metrics, and diverse training teams are essential safeguards.
Regulatory Compliance
GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, HIPAA in healthcare, and emerging AI regulations (EU AI Act, US Executive Order on AI) impose strict requirements on how AI systems are built, documented, and operated. Non-compliance risks fines up to 4% of global annual revenue under GDPR.
Best Practices for DS AI Success
Based on our experience with 50+ DS AI implementations, here are the practices that consistently separate successful projects from failed ones:
Start with a pilot project. Choose a high-impact, well-scoped problem for your first DS AI initiative. Success here builds organizational confidence and proves ROI before scaling.
Establish strong data governance. Define data ownership, quality standards, access controls, and lineage tracking before launching projects. This prevents 80% of data-related project delays.
Build cross-functional teams. The best DS AI teams include data engineers, data scientists, domain experts (e.g., doctors, financial analysts), product managers, and software engineers. Don't silo your data scientists.
Foster a data-driven culture. Invest in data literacy training for non-technical stakeholders. When business users understand and trust DS AI outputs, adoption rates soar.
Implement MLOps from day one. Version your code, data, and models. Use CI/CD pipelines for model deployment. Monitor production performance continuously.
Measure and communicate ROI clearly. Tie model metrics (accuracy, precision, recall) to business metrics (revenue, cost, time saved). Present results in the language of the boardroom, not the data lab.
Pro Tip
Don't let perfect be the enemy of good. A model that is 80% accurate and deployed in production delivering value beats a 99% accurate model stuck in development. Ship early, iterate often, and improve continuously.
Not sure where to start? Explore Samta.ai's Consulting & Strategy Services to build your DS AI roadmap with expert guidance.
The Future of Data Science AI (2026–2030)
DS AI is evolving faster than any technology in history. Here are the five trends that will define the next four years:
Explainable AI (XAI) Becomes Mandatory
Regulatory pressure particularly the EU AI Act and financial services regulations is making explainability a legal requirement for high-stakes AI decisions. Models must explain why they made a decision (loan denied, treatment recommended, fraud flagged). XAI tools like SHAP and LIME are becoming mainstream.
AutoML Democratizes AI Development
AutoML platforms (Google AutoML, AWS AutoPilot, H2O.ai) are making model building accessible to non-experts. By 2028, analysts with Excel skills will build production-grade ML models fundamentally changing the DS AI talent market.
Augmented Analytics
Business intelligence tools are embedding AI to auto-generate insights, anomaly alerts, and natural language explanations of data trends. Tableau AI, Power BI Copilot, and ThoughtSpot are leading this charge putting DS AI directly in the hands of business users.
Edge AI & IoT Integration
AI inference is moving from cloud data centers to devices smartphones, factory sensors, autonomous vehicles, medical devices. Edge AI eliminates latency, reduces bandwidth costs, and enables real-time decisions without internet connectivity.
Agentic AI Systems
The next frontier: AI agents that autonomously execute multi-step DS AI workflows collecting data, running analysis, deploying models, and reporting results with minimal human intervention. Platforms like LangChain Agents, AutoGen, and CrewAI are making this a reality in 2026.
FAQ
What's the difference between Data Science and Data Science AI?
Data Science is the broader discipline of extracting insights from data using statistics, programming, and domain knowledge. Data Science AI is a subset that specifically integrates AI technologies machine learning, deep learning, NLP into the data science workflow to automate predictions, enable learning systems, and scale decision-making beyond what human analysis alone can achieve. Traditional data science produces reports and insights; DS AI produces autonomous, continuously improving systems.Do I need coding skills to work with DS AI?
It depends on your role. Data scientists and ML engineers absolutely need Python (or R) skills. However, business analysts and decision-makers can leverage DS AI through no-code/low-code tools like Power BI AI features, Google Looker ML, or Tableau AI with minimal coding. For those entering the field technically, Python proficiency plus familiarity with Pandas, Scikit-learn, and SQL will cover 80% of daily DS AI work.How long does it take to implement a DS AI project?
Implementation timelines vary significantly by complexity. A simple classification model (e.g., lead scoring) can be built and deployed in 4–8 weeks. A complex recommendation engine or real-time fraud detection system typically takes 3–6 months. Enterprise-wide DS AI platform buildouts span 12–24 months. We recommend starting with a focused 8-week pilot to demonstrate value before committing to larger investments.What's the average ROI for DS AI initiatives?
According to McKinsey, high-performing companies achieve 3.5x ROI on AI investments within three years. However, ROI varies enormously by use case. Predictive maintenance typically delivers 200–400% ROI. Fraud detection systems in financial services often achieve 500–800% ROI. Marketing personalization yields 150–300% ROI. The key is selecting high-value use cases with clear, measurable business outcomes from the start.Is DS AI only for large enterprises?
Absolutely not. Cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP) have democratized access you can launch a fully functional ML pipeline for under $500/month. Pre-trained AI models from Hugging Face and OpenAI APIs let small businesses add sophisticated AI capabilities without building from scratch. In our experience, mid-size companies often see faster ROI than enterprises because they have less bureaucracy, faster decision cycles, and clearer problem ownership.
Conclusion: Your DS AI Journey Starts Here
Data Science AI is not a buzzword it's a business imperative. The organizations that are building DS AI capabilities today are creating compounding competitive advantages that will be nearly impossible to replicate in five years.
We've covered the complete landscape: what DS AI is, how it evolved, its core components, the 7-step process every successful project follows, the tools that power it, real-world applications generating measurable ROI, the challenges to anticipate, and the future trends to prepare for.
The question is no longer whether to invest in DS AI it's how quickly you can build the capabilities to compete.
Ready to Transform Your Business with DS AI?
Whether you're starting your first pilot project or scaling an enterprise AI platform, Samta.ai has the expertise, tools, and team to accelerate your journey. Our clients average 3.2x ROI within the first year of DS AI implementation.
Take your next step:
Explore our AI & Data Science Services — tailored solutions for your industry
Schedule a Free Consultation — 30 minutes with our expert team, no obligation
Key Takeaways
Summary
5 things to remember from this guide:
Data Science AI combines ML, deep learning, statistical modeling, and data engineering into a unified system for automated, scalable intelligent decision-making.
The 7-step DS AI process from problem definition to deployment and monitoring is the framework every successful AI project follows. Never skip steps.
Real ROI is achievable at every business size. Cloud platforms and pre-trained models make DS AI accessible to SMBs, not just enterprises.
The biggest DS AI failures share the same root causes: poorly defined problems, bad data quality, and neglected model monitoring.
The future belongs to XAI, AutoML, edge AI, and agentic systems organizations building DS AI capabilities today will have a decisive competitive advantage by 2030.
